The statistical sampling universe for our model was defined as vouchers submitted during FY 2002 for United States Marshal Service (USMS) prisoner medical services from 14 of the 94 USMS districts. The 14 districts selected accounted for 91.3 percent of the total dollar value of vouchers submitted. Our sample test results were projected only to the prisoner medical service activities in the 14 districts tested.
We used a random sampling method with stratified design to provide effective coverage of the units and to obtain precise estimates of the characteristics tested. Each unit was tested for multiple characteristics as discrete variables involving nominal measures. Statistical analysis was conducted on the test results of four variables. An explanation of the audit test results and relevance of the tests to the audit's objectives is provided in the body of the audit report. We present 95 percent confidence limits on the expected value of the proportions by using the formulae given at the end of this appendix.
From the universe of 6,525 vouchers, we selected as first stage sample units a random sample of 900 vouchers (an average of 64 vouchers per district). The random sample of 900 vouchers out of 6,525 provided a sampling fraction of 13.8 percent. From each of the randomly selected vouchers a random sample of up to 10 transactions (second stage sampling units) was tested. The sample test results were projected to the universe of transactions at the 14 USMS districts.
The table below provides the test results and projections for the random variables tested. Following the table are the mathematical model notations, and formulae used to compute the estimates of expected values and variances.
Test Results Projections for the Random Variables Tested
| Question (Variable Tested) |
Answer (Results of Test) |
Rate of Occurrence (%) |
Projection at 95 Percent Lower Confidence Limit* (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Was the prisoner in USMS custody during the treatment? | Yes | 94.5 | |
| No | 0.2 | 0.19 | ||
| Unk | 5.3 | 5.2 | ||
| 2. | Was the transaction accurately recorded? | Yes | 51.9 | |
| No | 1.0 | 0.99 | ||
| Unk | 47.1 | 47.0 | ||
| 3. | Was the transaction fully supported? | Yes | 67.8 | |
| No | 27.3 | 26.9 | ||
| Unk | 4.9 | 4.5 | ||
| 4. | Were the procedures necessary? | Yes | 69.7 | |
| No | 3.3 | 3.1 | ||
| Unk | 27.0 | 26.4 | ||
| *This is the most conservative projection at the 95 percent confidence level. In other words, the projected percentage is at least the percentage of occurrence present in the corresponding universe. |
Mathematical Model Notations and Formulae used to compute the Estimates of Expected Values and Variances
The mathematical model notations, and formulae used to compute the estimates of expected values, and the variances are as follows.
| H | The number of strata |
| Nh | The number of units in the stratum h, where |
|
| nh | The number of units sampled from the stratum h |
| yhijk | Variable k corresponding to jth selected item within the ith sampled item from the hth stratum |
| yhijkl = |
 |
|
|
| yhikl |
|
| phikl | Sample proportion of hits of lth type of the kth variable in the ith sampled item in hth stratum |
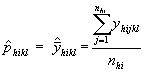 |
, |
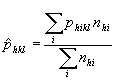 |
, and |
|
|
To compute the variance of the estimate
Where The 95 percent lower confidence limits on the estimate is given by |